ExoQuick-TC Exosome Precipitation Solution
Isolate exosomes from tissue culture media fast and scalable
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Product Category: | Exosome Precipitation |
| Sample Type: | Cell Culture Media & Biofluids |
Product Description
ExoQuick-TC can be used to purify exosomes from a wide variety of tissue culture media, and from certain biofluids such as saliva, urine, follicular fluid, and breast milk. ExoQuick-TC is a proprietary polymer that gently precipitates exosomes.
With a simple workflow involving minimal hands-on time and low input sample volume requirements, ExoQuick-TC is an excellent option for researchers who need to purify multiple exosome samples.
Features and Benefits
- Saves time and labor
- Is easily scalable
- Conserves precious sample
- Delivers high yields of functional, high quality exosomes
- Can be used to isolate exosomes for a wide range of downstream applications
Questions?
Connect with us today to get started with your exosome isolation.
Applications
- Biomarker studies
- Exosomal miRNA profiling
- Exosomal proteomics and lipidomics/metabolomics
- Functional studies, such as in cell-to-cell signaling, basic biology, such as role in tumorigenesis
How it works
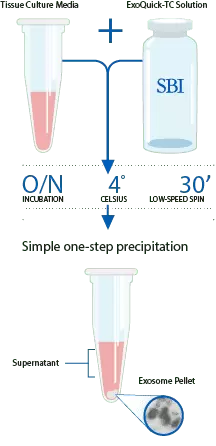
First, pre-clear your samples of cells and cellular debris, and then simply add the appropriate amount of ExoQuick-TC to your cleared biofluid, refrigerate, and centrifuge (see the product manual for protocol details). Your exosomes will be in the pellet, ready for resuspension in an appropriate solution.
To isolate exosomes from tissue culture media, simply:
- Add an appropriate volume of ExoQuick-TC
- Incubate overnight at 4°C
- Isolate exosomes with a 30-minute low-speed spin (1500g).
Choose the right ExoQuick for your application
| Application | Product |
| Purest EV isolation | ExoQuick ULTRA ExoQuick-TC ULTRA |
| General purpose EV isolation | ExoQuick ExoQuick-TC |
| EV isolation that removes contaminating lipoprotein particles from plasma or serum | ExoQuick-LP |
| EV isolation that includes a de-fibrinating plasma step prior to isolation | ExoQuick Plasma Prep with Thrombin |
Supporting Data
Characterizing ExoQuick-TC exosomes with NanoSight
Exosomes purified with ExoQuick-TC from tissue culture media show the expected particle size distribution and high concentration yields when analyzed using NanoSight’s Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA, Figure 2).
Figure 2. Exosome size distribution and yields from tissue culture media. Cells from a human HT1080 lung sarcoma cell line were cultured in conditioned media (serum-free) for 72 hours. 10 mL of media was combined with 2 mL ExoQuick-TC, incubated overnight at 4°C, and centrifuged at 1500g for 30 minutes to isolate exosomes. The exosome pellet was resuspended in 1 mL PBS, diluted 1:40, and visualized on the NanoSight LM10 instrument. The analysis shows that ExoQuick-TC recovered 133 nm exosomes at a concentration of 1.74 x 109 particles/mL.
More data of performance can be found in the ExoQuick-TC Product Sheet.
Any Questions Left?
Contact us for assistance to get started with your gentle and reliable exosome precipitation.
Product Citations
- Ali, SA;Singla, DK; (2024) Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland)
- Almouh, M;Pakravan, K;Ghazimoradi, MH;Motamed, R;Bakhshinejad, B;Hassan, ZM;Babashah, S; (2024) Exosomes released by oxidative stress-induced mesenchymal stem cells promote murine mammary tumor progression through activating the STAT3 signaling pathway Molecular and cellular biochemistry
- Aloy, N;Coughlan, C;Graner, M;Witt, S; (2024) Possible regulation of the immune modulator tetraspanin CD81 by alpha-synuclein in melanoma bioRxiv
- Aoki, S;Inoue, Y;Hamazaki, M;Hara, S;Noguchi, T;Shirasuna, K;Iwata, H; (2024) miRNAs in Follicular and Oviductal Fluids Support Global DNA Demethylation in Early-Stage Embryos International Journal of Molecular Sciences
- Banerjee, S;Sharma, V;Das Mukhopadhyay, C; (2024) Exploring emerging concepts of exosomes for the diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics of brain cancers Extracellular Vesicle

