FFPE Total RNA Purification Kit
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Product Category: | Total RNA incl. microRNA Purification |
| Sample Type: | FFPE Tissue Samples |
Product Description
- Extract total RNA (large mRNA, rRNA, microRNA, siRNA) from FFPE samples
- Rapid spin column format
- No phenol:chloroform extraction step
- Isolated RNA is of high yield, quality and integrity
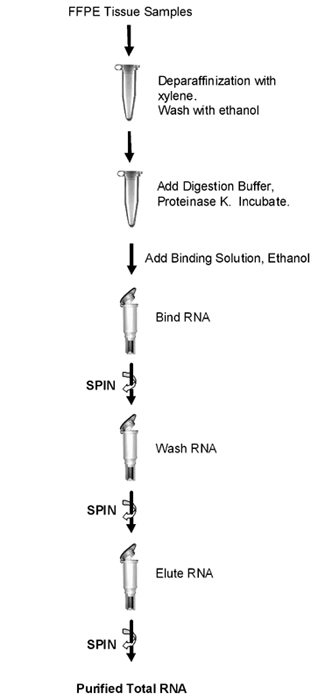
Norgen’s FFPE RNA Purification Kit provides a rapid method for the isolation and purification of total RNA (including microRNA) from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples.
Using formalin to fix tissues leads to crosslinking of the RNA and proteins, and the process of embedding the tissue samples can also lead to fragmentation of the RNA over time. Norgen’s FFPE RNA Purification Kit provides conditions that allow for the partial reversing of the formalin modifications, resulting in a high quality and yield of RNA.
The kit is able to purify all sizes of RNA, from large mRNA and ribosomal RNA down to microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA), depending on the age of the FFPE tissue as fragmentation of the RNA is known to occur over time.
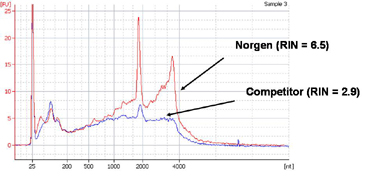
Figure 1: High Quality and Yield of Total RNA
Total RNA was isolated from equal amounts of an FFPE tissue sample using Norgen’s FFPE RNA Purification Kit and a leading competitor's kit. The purified RNA was then resolved on an Agilent BioAnalzyer. As it can be seen, Norgen not only isolated higher yields of total RNA, but the RNA was also of a higher quality as evidenced by the higher RIN values obtained with Norgen’s RNA.
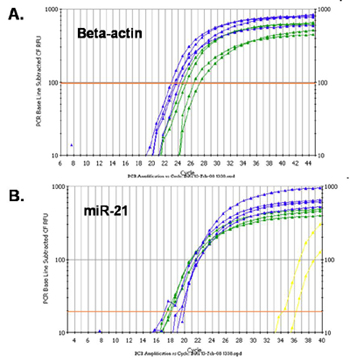
Figure 2: High Yield of a Diversity of RNA Species
Total RNA was isolated from equal amounts of an FFPE tissue sample using Norgen’s FFPE RNA Purification Kit and a leading competitors kit. The purified RNA was then used as the template in a RT-qPCR for detecting the beta-actin gene (Panel A) and for detecting miR-21(Panel B). In both graphs the blue lines correspond to Norgen isolated-RNA and the green lines correspond to competitor-isolated RNA. As it can be seen, Norgen’s kit isolated higher yields of RNA in both cases, as indicated by the higher C T values of the blue lines. Also, Norgen’s kit successfully isolated not only large RNA (Panel A) but also microRNA (Panel B), indicating the diversity of RNA species isolated.
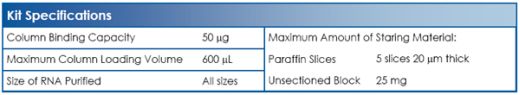
FFPE RNA Kit Specifications (per prep)
FFPE RNA Kit Applications
- qRT-PCR and RT-PCR
- Expression Array Profiling
- Primer Extension
Product Citations
- Dini, P., Carossino, M., Loynachan, A. T., El-Sheikh Ali, H., Wolfsdorf, K. E., Scoggin, K. E., Daels, P., & Ball, B. A. (2020) Equine hydrallantois is associated with impaired angiogenesis in the placenta. Placenta
- Haughey, C. M., Mukherjee, D., Steele, R. E., Popple, A., Dura-Perez, L., Pickard, A., Jain, S., Mullan, P. B., Williams, R., Oliveira, P., Buckley, N. E., Honeychurch, J., McDade, S., Illidge, T., Mills, I. G., & Eddie, S. L. (2020) Development of a novel allograft model of prostate cancer: a new tool to inform clinical translation [Preprint].
- Haughey, C. M., Mukherjee, D., Steele, R. E., Popple, A., Dura-Perez, L., Pickard, A., Patel, M., Jain, S., Mullan, P. B., Williams, R., Oliveira, P., Buckley, N. E., Honeychurch, J., S. McDade, S., Illidge, T., Mills, I. G., & Eddie, S. L. (2020) Investigating Radiotherapy Response in a Novel Syngeneic Model of Prostate Cancer Cancers
- Lau, R., Du, L., Chen, E., Fu, C., Gould, R., Marczyk, M., Sinn, B. V., Layman, R., Bedrosian, I., Valero, V., & Symmans, W. F. (2020) Technical Validity of a Customized Assay of Sensitivity to Endocrine Therapy Using Sections from Fixed Breast Cancer Tissue Clinical Chemistry
- Luchetti, M. M., Ciccia, F., Avellini, C., Benfaremo, D., Rizzo, A., Spadoni, T., Svegliati, S., Marzioni, D., Santinelli, A., Costantini, A., Viola, N., Berretta, A., Ciferri, M., Mattioli Belmonte Cima, M., Mosca, P., Benedetti, A., & Gabrielli, A. (2020) Gut epithelial impairment, microbial translocation and immune system activation in inflammatory bowel disease–associated spondyloarthritis Rheumatology
- Catalog Number
25300-NB - Supplier
Norgen Biotek - Size
- Shipping
RT
You save 10 %
494,00 €
