ChromaFlash High Sensitivity ChIP Kit
For immunoprecipitation of chromatin (ChIP) from small amounts of mammalian cells or tissues
Product Description
The ChromaFlash™ High-Sensitivity ChIP Kit is a complete set of optimized reagents to carry out a successful chromatin immunoprecipitation procedure in a high throughput format starting from mammalian cells or tissues. The highly specific and sensitive kit is suitable for selective enrichment of a chromatin fraction containing specific DNA sequences using various mammalian cell/tissues. The optimized protocol and kit components reduce non-specific background ChIP levels to allow capture of low abundance protein/transcription factors and increased specific enrichment of target protein/DNA complexes. The target protein bound DNA prepared with the ChromaFlash™ High-Sensitivity ChIP Kit can be used for various downstream applications including PCR (ChIP-PCR), microarrays (ChIP-on-chip), and sequencing (ChIP-seq). The kit has the following advantages:
- The highly efficient enrichment ratio of positive to negative control is > 500. An extremely low number of cells (as low as 2,000 cells per ChIP reaction) can be used for enriching highly abundant protein/DNA complexes.
- Optimized buffers and protocol allow minimal ChIP background by overcoming the weaknesses that cause non-specific enrichment, thereby increasing sensitivity and specificity of the ChIP reaction.
- Increased antibody selectivity and capture efficiency through the use of unique chimeric proteins containing the maximum number of IgG binding domains coated on the strip-wells. This allows strong binding of any IgG subtype antibodies within a wide pH range regardless if they are in monoclonal or polyclonal form.
- Fast 5 hour procedure, from input chromatin to ready-to-use DNA eluate.
- 96-well plate format makes the assay flexible. Either (a) manual with one single reaction each time; or (b) high throughput with 24-48 reactions each time.
- Wide downstream analysis compatibility. Compatible with various downstream analysis workflows including ChIP-PCR, ChIP-on-chip, and ChIP-seq.
See also a quick chart to compare ChIP kits.
Background Information
Protein-DNA interaction plays a critical role for cellular functions such as signal transduction, gene transcription, chromosome segregation, DNA replication and recombination, and epigenetic silencing. Identifying the genetic targets of DNA binding proteins and knowing the mechanisms of protein-DNA interaction is important for understanding cellular processes. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) offers an advantageous tool for studying such protein-DNA interactions. It allows for the detection of a specific protein bound to a specific gene sequence in living cells using PCR (ChIP-PCR), microarrays (ChIP-chip), or sequencing (ChIP-seq). For example, measurement of the amount of methylated histone H3 at lysine 9 (meH3-K9) associated with a specific gene promoter region under various conditions can be achieved through a ChIP-PCR assay, while the recruitment of methylated H3-K9 to the promoters on a genome-wide scale can be detected by ChIP-on-chip or ChIP-sequencing. ChIP analysis requires that ChIPed DNA contains minimal background in order to reliably identify true TF-enriched regions. High background in ChIP is mainly caused ineffective wash buffers, insufficient cross-link reversal, inappropriate DNA fragment length, and residual RNA interference. To effectively capture TF/DNA complexes, which are often in low abundance, an ideal ChIP method requires having maximum sensitivity with minimized background levels. This method should also be able to enrich highly abundant protein/DNA complexes using a small amount of cells or tissues in a high throughput format. Epigentek’s ChromaFlash™ High-Sensitivity ChIP Kit is designed to achieve these goals by maximizing sensitivity and minimizing non-specific background signals.
Principle & Procedure

This ChIP kit includes a positive control antibody (RNA polymerase II), a negative control non-immune IgG, and GAPDH primers that can be used as a positive control to demonstrate the efficacy of the kit reagents and protocol. RNA polymerase II is considered to be enriched in the GAPDH gene promoter that is expected to be undergoing transcription in most growing mammalian cells and can be immunoprecipitated by a RNA polymerase II antibody but not by non-immune IgG. Immunoprecipitated DNA is then cleaned, released, and eluted. Eluted DNA can be used for various downstream applications such as ChIP-PCR, ChIP-on-chip, and ChIP-seq.
Starting Materials
Starting materials can include various tissue or cell samples such as cells from flask or plate cultured cells, fresh and frozen tissues, etc. In general, the amount of cells and tissues for each reaction can be 2 x 103 to 1 x 106 and 0.5 mg to 50 mg, respectively. For optimal preparation, the input amount should be 1 to 2 x 105 cells or 10 to 20 mg tissues since the enrichment of target proteins to genome loci may vary. For the target proteins that are low abundance transcription factors, the input amount should be 5 to 6 x 105 cells or 50 to 60 mg tissues.
Performance Data
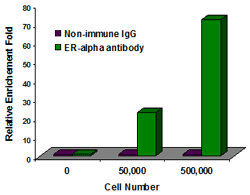
Fig.2. Low abundance protein enrichment: Sheared chromatin isolated from different numbers of MCF-7 cells was used for ChIP-qPCR analysis of ER-a enrichment in TFF1 promoters using the ChromaFlash High-Sensitivity ChIP Kit (Cat. No. P-2027) and the EpiQuik Quantitative PCR Fast Kit (Cat. No. P-1029).
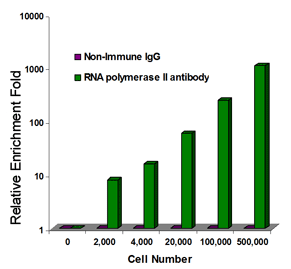
Fig.3. High abundance protein enrichment: Sheared chromatin isolated from different numbers of MBD-231 cells was used for ChIP-qPCR analysis of RNA polymerase II enrichment in GAPDH promoters using the ChromaFlash High-Sensitivity ChIP Kit (Cat. No. P-2027) and the EpiQuik Quantitative PCR Fast Kit (Cat. No. P-1029).
Product Citations
- Kang YY, Kim DY, Lee SY, Kim HJ, Kim T, Cho JA, Lee T, Choi EY (2024) Innate Immune Training Initiates Efferocytosis to Protect against Lung Injury. Adv Sci (Weinh)
- Matsuda KM, Kotani H, Hisamoto T, Kuzumi A, Fukasawa T, Yoshizaki-Ogawa A, Sato S, Yoshizaki A (2024) Dual blockade of interleukin-17A and interleukin-17F as a therapeutic strategy for liver fibrosis: Investigating the potential effect and mechanism of brodalumab. Cytokine
- Xiao C, Li Y, Liu Y, Dong R, He X, Lin Q, Zang X, Wang K, Xia Y, Kong L (2024) Overcoming Cancer Persister Cells by Stabilizing the ATF4 Promoter G-quadruplex. Adv Sci (Weinh)
- Fang A, Yuan Y, Sui B, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Zhou M, Chen H, Fu ZF, Zhao L (2023) Inhibition of miR-200b-3p confers broad-spectrum resistance to viral infection by targeting TBK1. mBio
- Kapuganti RS, Sahoo L, Mohanty PP, Hayat B, Parija S, Alone DP (2023) Role of clusterin gene 3'-UTR polymorphisms and promoter hypomethylation in the pathogenesis of pseudoexfoliation syndrome and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech

